Supply chain management sets the stage for efficient business operations by defining its components and objectives. Dive into the world of supply chains with a mix of cool and informative vibes that will keep you hooked from the get-go.
Get ready to uncover the strategies, technologies, and risk management tactics that drive successful supply chains in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Introduction to Supply Chain Management
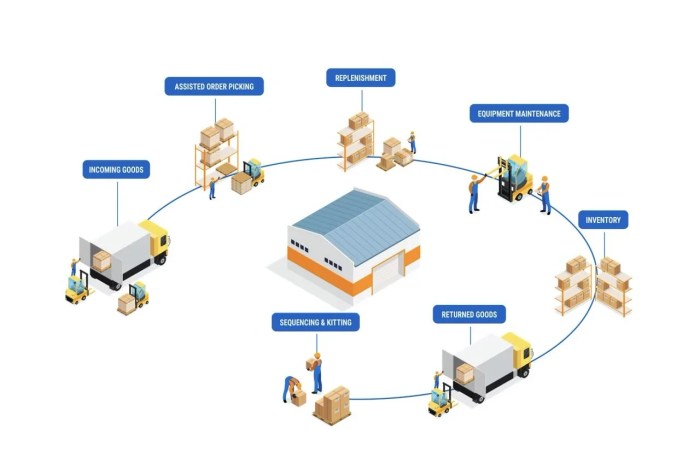
Supply chain management is the coordination and oversight of the flow of goods, information, and finances as they move from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer. It plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of businesses and meeting customer demand efficiently.
Key Components of a Supply Chain
- Suppliers: Provide raw materials or components needed for production.
- Manufacturers: Transform raw materials into finished products.
- Distributors: Transport and store finished products before reaching retailers.
- Retailers: Sell products directly to consumers.
Objectives of Effective Supply Chain Management
- Cost Efficiency: Minimize costs associated with production, transportation, and inventory management.
- Improved Customer Service: Ensure timely delivery of products to meet customer demands.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Foster strong relationships with suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors for seamless operations.
Supply Chain Strategies
In the world of supply chain management, various strategies are utilized to optimize processes and ensure efficiency. Three key strategies commonly used are lean, agile, and responsive supply chain strategies. Each strategy comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different scenarios and industries.
Lean Supply Chain Strategy
The lean supply chain strategy focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency in operations. By streamlining processes and reducing excess inventory, companies can lower costs and improve overall productivity. One example of a company successfully implementing a lean strategy is Toyota, known for its efficient production system that emphasizes continuous improvement and waste reduction.
Agile Supply Chain Strategy
On the other hand, the agile supply chain strategy prioritizes flexibility and responsiveness to changing market demands. Companies that adopt an agile approach are able to quickly adapt to fluctuations in demand and supply, ensuring customer satisfaction and competitive advantage. An example of a company known for its agile supply chain is Zara, a fast-fashion retailer that can quickly bring new designs to market based on real-time data and customer feedback.
Responsive Supply Chain Strategy
Lastly, the responsive supply chain strategy combines elements of both lean and agile strategies to create a balanced approach. This strategy aims to be efficient while also being able to respond rapidly to market changes and customer needs. Apple is a prime example of a company that has successfully implemented a responsive supply chain strategy, with its ability to efficiently manage global operations while quickly adapting to new product launches and consumer trends.
Technology in Supply Chain Management
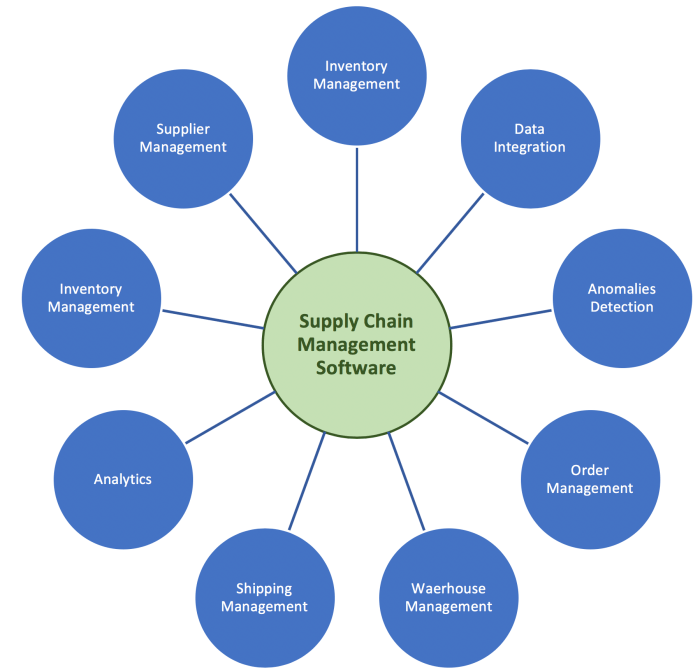
Technology such as IoT, AI, and blockchain is revolutionizing the way supply chain management operates. These innovative solutions are streamlining processes, increasing efficiency, and enhancing visibility across the entire supply chain.
IoT in Supply Chain Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) enables devices to communicate and share data in real-time, allowing for better tracking and monitoring of inventory, shipments, and equipment. This connectivity improves decision-making, reduces errors, and enhances overall supply chain visibility.
AI in Supply Chain Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is being used to analyze vast amounts of data, predict demand, optimize routes, and automate routine tasks. By leveraging AI algorithms, companies can make more informed decisions, improve forecasting accuracy, and enhance operational efficiency.
Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology ensures transparency, security, and immutability of data along the supply chain. It enables seamless tracking of goods, facilitates trust among partners, and prevents fraud. By utilizing blockchain, organizations can create a more trustworthy and efficient supply chain ecosystem.
Benefits of Using Technology in Supply Chain Management
- Improved Visibility: Technology allows for real-time tracking of inventory, shipments, and processes, leading to enhanced visibility and control.
- Increased Efficiency: Automation and AI-driven solutions optimize operations, reduce lead times, and minimize costs.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Technologies like blockchain foster trust and collaboration among supply chain partners, leading to smoother operations and better decision-making.
Challenges and Risks of Implementing Technology in Supply Chains, Supply chain management
- Data Security Concerns: With the increased use of technology comes the risk of cyber threats and data breaches, requiring robust security measures to safeguard sensitive information.
- Integration Complexity: Implementing new technologies may require significant changes to existing systems and processes, posing challenges in integration and adoption.
- Cost and ROI: Investing in technology can be costly, and organizations must carefully evaluate the return on investment to ensure the benefits outweigh the expenses.
Supply Chain Risk Management
Supply chain risk management is crucial for businesses to identify and address potential disruptions in their supply chain. Common risks include demand variability, supplier issues, and geopolitical factors that can impact the flow of goods and services.
Mitigating Supply Chain Risks
- Implementing data analytics to forecast demand and reduce variability.
- Diversifying suppliers to minimize the impact of supplier issues.
- Conducting risk assessments and scenario planning to prepare for geopolitical uncertainties.
Maintaining Supply Chain Resilience
- Establishing strong supplier relationships to ensure open communication and collaboration.
- Investing in technology solutions like blockchain for greater transparency and traceability.
- Creating a contingency plan with alternative sourcing options in case of disruptions.
Examples of Overcoming Supply Chain Disruptions
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, companies like Apple shifted production to other regions and increased safety measures to ensure continuity.
- Nike faced supplier issues in the past but worked closely with partners to resolve them and improve supply chain visibility.
- The Suez Canal blockage in 2021 led companies to reroute shipments and reassess their logistics strategies to minimize delays.